Koshi
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

Landslide data of Koshi basin is digitized from topo sheets published in 1990s.
-

Landslide data of Koshi basin was digitized from Landsat and Googel Earth.
-
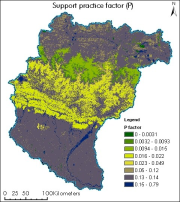
The dataset showing support practice factor of Koshi basin. It represents the soil conservation operations or other measures that control the erosion. It is measured as the ratio of soil loss with a specific support practice to the corresponding loss with ploughing up and down slope (Renard et al., 1997b; Prasannakumar et al., 2012).
-

Accelerated soil erosion is a common and environmentally destructive consequence of development in the populated trans-boundary Koshi river basin. The objective of this study was to assess assessment of soil erosion pattern and dynamic change trend of spatial distribution in erosion status between 1990 and 2010 and obtained the conservation priority map in the Koshi basin area using GIS and remote sensing. To develop soil erosion pattern revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) were adopted in ArcGIS environment where is the rainfall erosivity, soil erodibility, slope length factor, crop management factor and support practice factors were used a primary parameters. This study result the annual total erosion 4,35,996 ton/ha/yr in 2010.
-
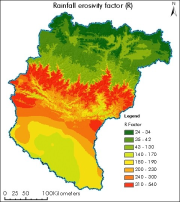
Digital polygon dataset of rainfall erosivity factor (R) of Koshi basin. The dataset is created using rainstorms of Nepal, India and China from world climate precipitation data. R-factor is computed as the average annual sum of the erosivity of the individual rainstorms, which is calculated as the product of total storm energy and maximum 30-min intensity. R-factor was evaluated from world climate precipitation data with equation (Renard and Freimund, 1994): R = 0.0483*P1.610 where P= annual precipitation (mm).
-

Land cover and its change analysis across Hindu Kush Himalayan region is realized as an urgent need to support diverse issues of environmental conservation. This study presents the first and most complete national land cover database of Koshi basin prepared using public domain Landsat TM data of 2010 and replicable methodology.The study estimated that Koshi basin is covered 19% by forests. The potential use of the data set for basin level sustainable land use planning strategies and meeting several global commitments also highlighted.
-

High levels of water-induced erosion in the transboundary Himalayan river basins are contributing to substantial changes in basin hydrology and inundation. Basin-wide information on erosion dynamics is needed for conservation planning, but field-based studies are limited. This study used remote sensing (RS) data and a geographic information system (GIS) to estimate the spatial distribution of soil erosion across the entire Koshi basin. The revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) was used in an ArcGIS environment with rainfall erosivity, soil erodibility, slope length and steepness, cover-management, and support practice factors as primary parameters. The estimated annual erosion from the basin was around 42 million tonnes.
-
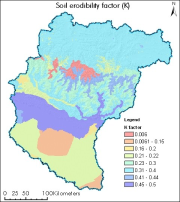
Digital polygon dataset of soil erosivity on Koshi Basin. The dataset is created using Soil maps of Nepal, India and FAO and represents the average long term soil response to the erosive power associated with rainfall and runoff. It shows a measure of the susceptibility of soil particles to detachment and transport by rainfall and runoff.
-

High levels of water-induced erosion in the transboundary Himalayan river basins are contributing to substantial changes in basin hydrology and inundation. Basin-wide information on erosion dynamics is needed for conservation planning, but field-based studies are limited. Part of the remote sensing (RS) and a geographic information system (GIS) based soil erosion estimation and spatial distribution of across the entire Koshi basin, a land cover map of 1990 used as a Support practice factor (PL). Land cover data for 1990 were prepared from analysis of the Landsat images using object-based image analysis.
-

High levels of water-induced erosion in the transboundary Himalayan river basins are contributing to substantial changes in basin hydrology and inundation. Basin-wide information on erosion dynamics is needed for conservation planning, but field-based studies are limited. This study used remote sensing (RS) data and a geographic information system (GIS) to estimate the spatial distribution of soil erosion across the entire Koshi basin. The revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) was used in an ArcGIS environment with rainfall erosivity, soil erodibility, slope length and steepness, cover-management, and support practice factors as primary parameters. The estimated annual erosion from the basin was around 42 million tonnes.
 Metadata Catalogue
Metadata Catalogue