Kabul
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The glacial lakes of Afghanistan were mapped using Landsat image that were selected based in a one-year buffer surrounding a representative year. For instance, the Landsat images from 1989 to 1991 were used to represent 1990 depending on the quality of images (least snow cover and cloud cover). The glacial lakes were extracted semi-automatically through an object-based image classification (OBIC) method and were then subjected to manual editing for quality control. The attributes of the data were extracted from the SRTM DEM. This dataset was produced in collaboration between the National Water Affairs Regulation Authority (NWARA) of the Government of Afghanistan and ICIMOD as part of the SERVIR-HKH Initiative.
-

The glacial lakes of Afghanistan were mapped using Landsat image that were selected based in a one-year buffer surrounding a representative year. For instance, the Landsat images from 2014 to 2016 were used to represent 2015 depending on the quality of images (least snow cover and cloud cover). The glacial lakes were extracted semi-automatically through an object-based image classification (OBIC) method and were then subjected to manual editing for quality control. The attributes of the data were extracted from the SRTM DEM. This dataset was produced in collaboration between the National Water Affairs Regulation Authority (NWARA) of the Government of Afghanistan and ICIMOD as part of the SERVIR-HKH Initiative.
-
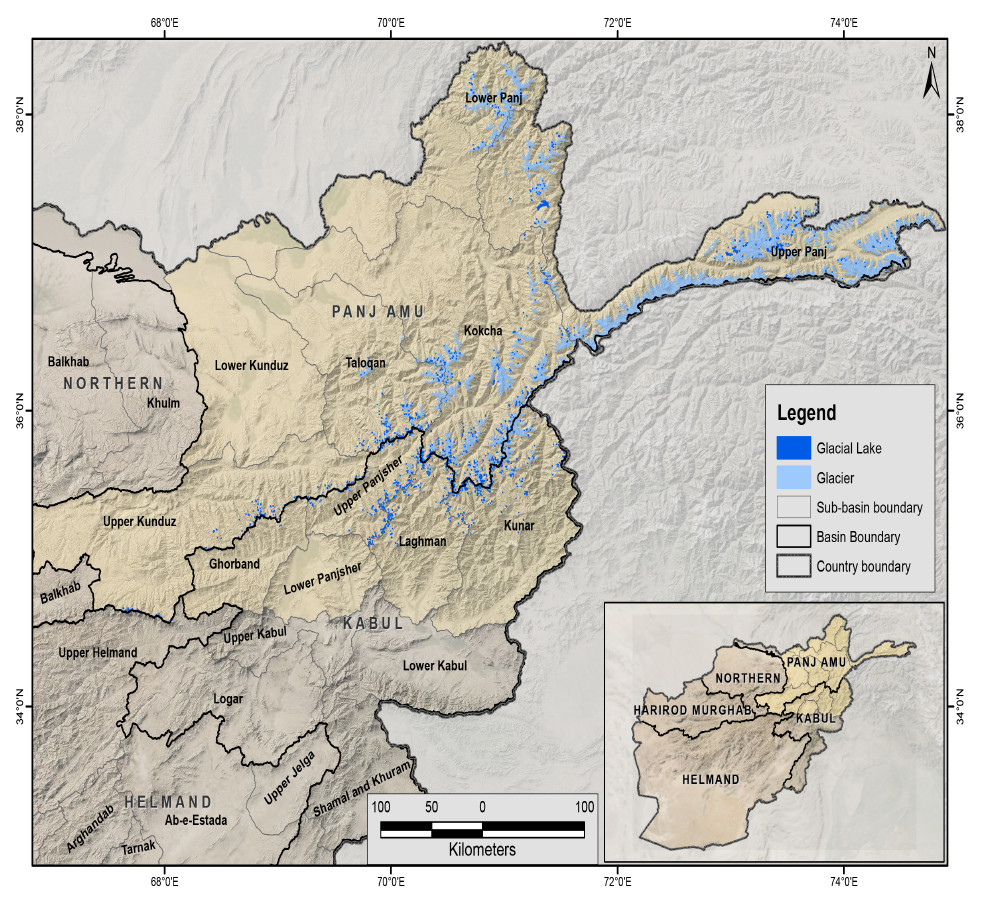
The glacial lakes of Afghanistan were mapped using Landsat image that were selected based in a one-year buffer surrounding a representative year. For instance, the Landsat images from 1999 to 2001 were used to represent 2000 depending on the quality of images (least snow cover and cloud cover). The glacial lakes were extracted semi-automatically through an object-based image classification (OBIC) method and were then subjected to manual editing for quality control. The attributes of the data were extracted from the SRTM DEM. This dataset was produced in collaboration between the National Water Affairs Regulation Authority (NWARA) of the Government of Afghanistan and ICIMOD as part of the SERVIR-HKH Initiative.
-

The glacial lakes of Afghanistan were mapped using Landsat image that were selected based in a one-year buffer surrounding a representative year. For instance, the Landsat images from 2009 to 2011 were used to represent 2010 depending on the quality of images (least snow cover and cloud cover). The glacial lakes were extracted semi-automatically through an object-based image classification (OBIC) method and were then subjected to manual editing for quality control. The attributes of the data were extracted from the SRTM DEM. This dataset was produced in collaboration between the National Water Affairs Regulation Authority (NWARA) of the Government of Afghanistan and ICIMOD as part of the SERVIR-HKH Initiative.
-

Glacier data of Afghanistan were prepared on the basis of Landsat imageries from 2010. The glacier outlines were derived semi-automatically using object-based image classification (OBIC) separately for clean-ice and debris-covered glaciers and further manual editing for quality assurance. The attributes of glacier data were derived from SRTM DEM. This dataset was jointly prepared by the Ministry of Energy and Water (MEW), Government of Afghanistan, and ICIMOD under the SERVIR-HKH Initiative.
-

Glacier data of Afghanistan were prepared on the basis of Landsat imageries from 1990. The glacier outlines were derived semi-automatically using object-based image classification (OBIC) separately for clean-ice and debris-covered glaciers and further manual editing for quality assurance. The attributes of glacier data were derived from SRTM DEM. This dataset was jointly prepared by the Ministry of Energy and Water (MEW), Government of Afghanistan, and ICIMOD under the SERVIR-HKH Initiative.
-

Glacier data of Afghanistan were prepared on the basis of Landsat imageries from 2000. The glacier outlines were derived semi-automatically using object-based image classification (OBIC) separately for clean-ice and debris-covered glaciers and further manual editing for quality assurance. The attributes of glacier data were derived from SRTM DEM. This dataset was jointly prepared by the Ministry of Energy and Water (MEW), Government of Afghanistan, and ICIMOD under the SERVIR-HKH Initiative.
-

Glacier data of Afghanistan were prepared on the basis of Landsat imageries from 2015. The glacier outlines were derived semi-automatically using object-based image classification (OBIC) separately for clean-ice and debris-covered glaciers and further manual editing for quality assurance. The attributes of glacier data were derived from SRTM DEM. This dataset was jointly prepared by the Ministry of Energy and Water (MEW), Government of Afghanistan, and ICIMOD under the SERVIR-HKH Initiative.
-
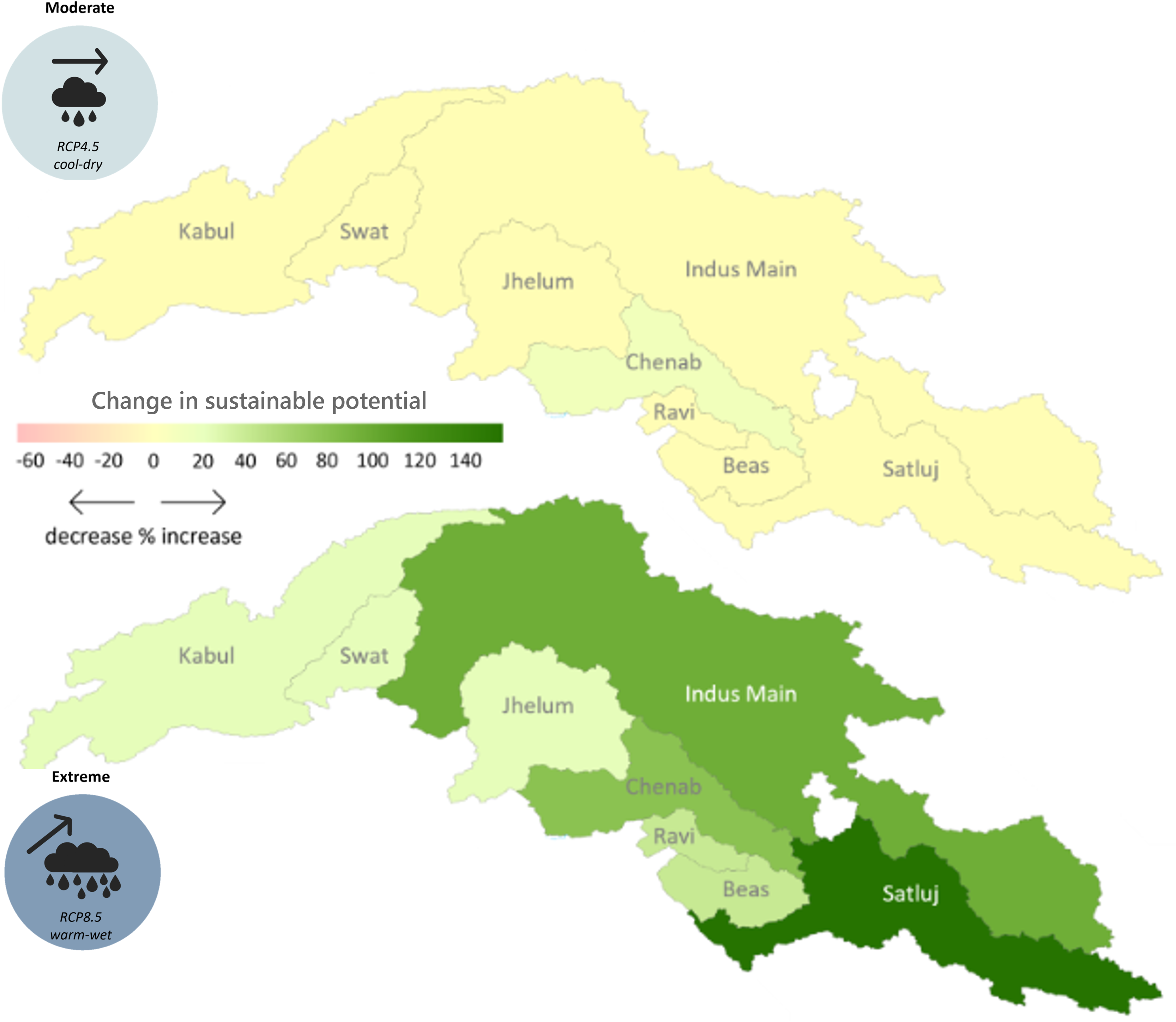
The hydropower potential in the upper Indus basin under future hydro-climatology was prepared using the Hydropower Potential Exploration (HyPE) as part of Work Package 2 in the SustainIndus project. Under future hydro-climatology, the HyPE model was run to explore theoretical potential followed by technical, financial and sustainable potential under policy assumptions for the mixed energy focus scenarios and risk-averse geo-hazard risk representation. In total, 72 future scenarios are considered combining CMIP6 model ensembles for 2 future time horizons (Mid: 2036-2065, Far: 2066-2095), 3 Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP 4.5, 7.0 and 8.5), 4 corner Global Climate Models for each RCP (Cold Dry, Cold Wet, Warm Dry, Warm Wet) and 3 Hydropower Potential classes (Technical, financial and sustainable).
-
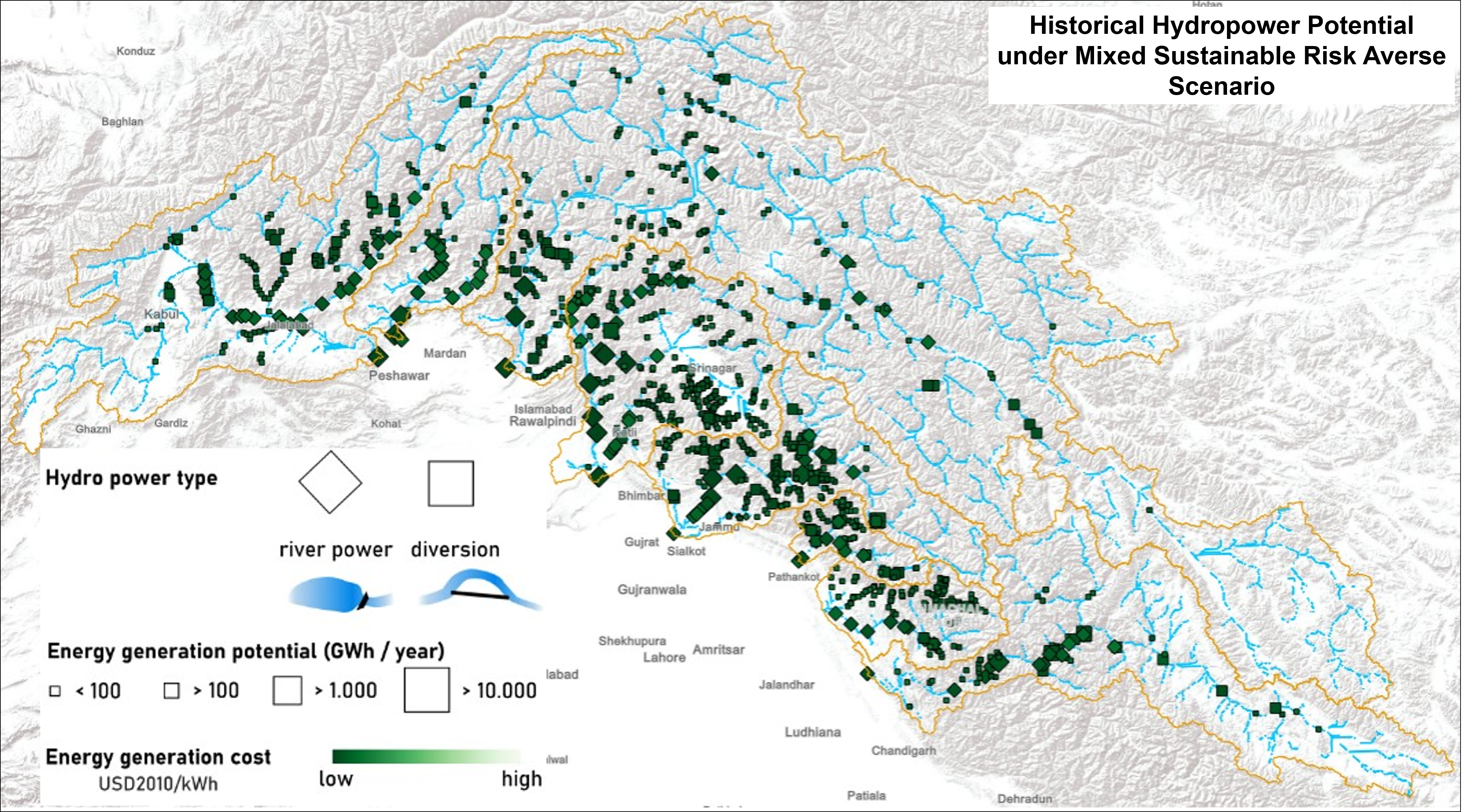
The hydropower potential in the upper Indus basin under historical hydro-climatology was prepared using the Hydropower Potential Exploration (HyPE) model. Under historical hydro-climatology, the HyPE model was run to explore theoretical potential followed by technical, financial and sustainable potential under two types of hydropower development policy scenarios. The energy focus scenarios (Large/Medium/Mixed) explored the impact of different scales of hydropower development. Additionally, for sustainable potential, the geo-hazard risk representation scenarios (Risk-averse/Cost-based/Multi-hazard) evaluated three ways to represent geo-hazard risk in hydropower development policies. Furthermore, historical analysis quantified technical, financial and sustainable potential under full and remaining cases. This dataset was produced under WorkPackage 2 of the SustainIndus project.
 Metadata Catalogue
Metadata Catalogue